by Guest Blogger Extraodinaire- Robert Kourik, author of Your Edible Landscape Naturally
As organic gardeners, we’re always looking for natural and non-harmful ways to add nutrient to the soil to aid in plant growth. One of the most important nutrients and one of the hardest to find in organic form is Nitrogen. Nitrogen encourages leafy growth and fruit and seed production. As plants grow, they take nitrogen out of the soil and it needs to be replaced. But how? Growing nitrogen fixing plants is one of the best ways to restore it in the soil. But this takes time. Compost and manures, which are also excellent for the plants, have relatively small amounts of nitrogen.
Blood meal is a fast-acting, high nitrogen, organic fertilizer. It is concentrated and often thought of as “hot”, meaning too much can hurt tender root hairs or roots. Often just a light sprinkling is enough. It can have a nitrogen content of 12.%, 1.00% phosphorus and 0.60% potassium. It can also attract dogs, racoons, possums and other meat eating animals that will dig up the garden beds. Blood meal, as you would expect, is a byproduct of the animal butchering industry. It takes a lot of energy to create blood meal in the form we use it in the garden. We also don’t know how the animals were raised. So it’s a bit of a stretch to call it “all natural and organic” in the way we want it to be safe and harmless to nature.
By knowing what blood meal is and where it comes from, you can make an informed decision about whether to use it or not.
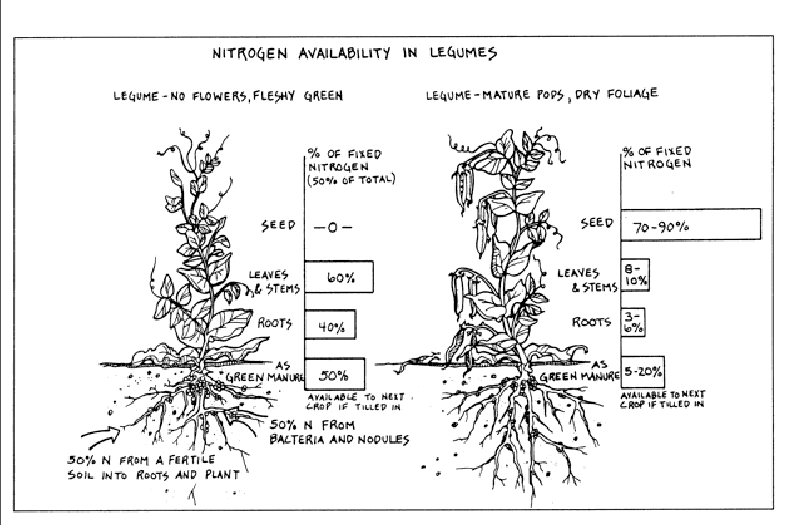
You can save energy by growing a legume crop solely for the accumulation of nitrogen in the lumpy nodules located on its roots—fertilizer gathered free from the nitrogen in the air. Legumes that produce enough nitrogen for hungry crops (like corn) are alfalfa, fava beans, clover and peas. Till under the young foliage before it blooms—called green manuring. This will increase the yield of crops without using blood meal. Use green manuring of any legume in any annual vegetable bed.
You can read more about fertilizers and everything else you might want to plant in the edible landscape in Robert Kourik’s book, Designing and Maintaining your Edible Landscape Naturally, at his website: www.robertkourik.com

 Follow
Follow