
by Avis Licht
Nitrogen is absolutely vital to plant health, and legumes are the plant world’s way of taking nitrogen out of the atmosphere and putting it into the soil. I think that’s pretty amazing. Therefore, legumes are a gardener’s best friend. Next to rain, which of course is our best, best friend. I’ve written on how rain also brings down nitrogen from the air to the soil for plant use. This is also amazing. But that’s nature for you.Most nitrogen in the world is in the form of a gas – which most plants can’t use. However, legumes, which are in the pea family, grab nitrogen from the air and store it in their roots on nodules. It’s actually a bacterium call Rhizobium that converts the nitrogen gas into a form that will be released into the soil that plants can use. This bacteria occurs naturally in the soil. You can increase the amount of nitrogen that a plant will fix by adding more of this bacteria, known as an inoculant. You can buy coated seed or buy the rhizobium and coat your own seed. You can find out more about them from Peaceful Valley Farm Supply
The most commonly grown legumes for nitrogen fixing are alfalfa, clover, fava beans, vetch and peas. The best time to harvest your legumes is BEFORE they flower and form seed pods. The pods take up most of the nitrogen. You can cut the plant at the base, leaving the roots in the ground and either put the green tops into the compost pile, or work the greens into the ground. If you put the “green manure” into the ground it will release the nitrogen over time. Initially the nitrogen will not be available to your next crop because it will be tied up in the decomposition process. What this means is that you should plan ahead for legume planting, so that you have time for the greens to break down in the soil before planting your next crop. Legumes make a wonderful cover crop for the winter, and at the same time prepare your soil for spring planting. If you need to plant immediately, I suggest you put the greens on the compost pile, leaving the roots in the ground.
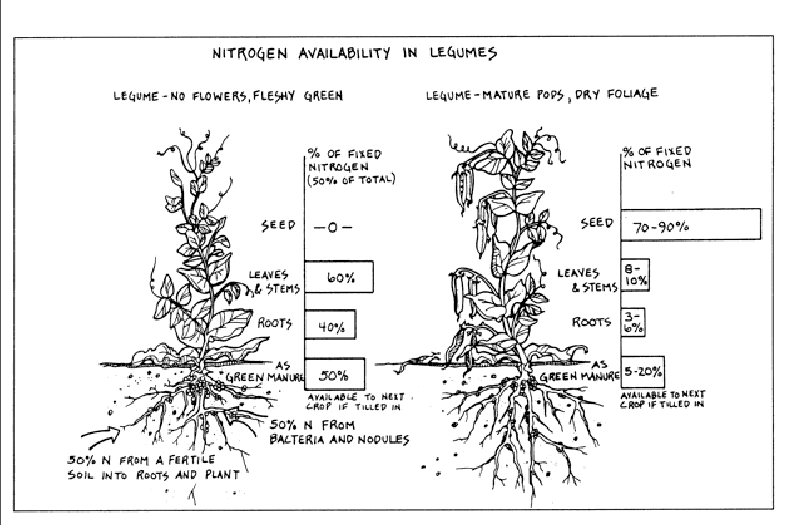
This diagram shows the difference in nitrogen availability in young and old plants. It is from Robert Kourik's book, Designing and Maintaining Your Edible Landscape (used with permission)
There will be more information on organic fertilizers in the next few posts. Subscribe to my blog and you won’t miss any of this useful information. Robert Kourik will tell you about blood meal – the pros and cons. Find out about other safe and interesting ways to fertilize your garden organically.

 Follow
Follow


